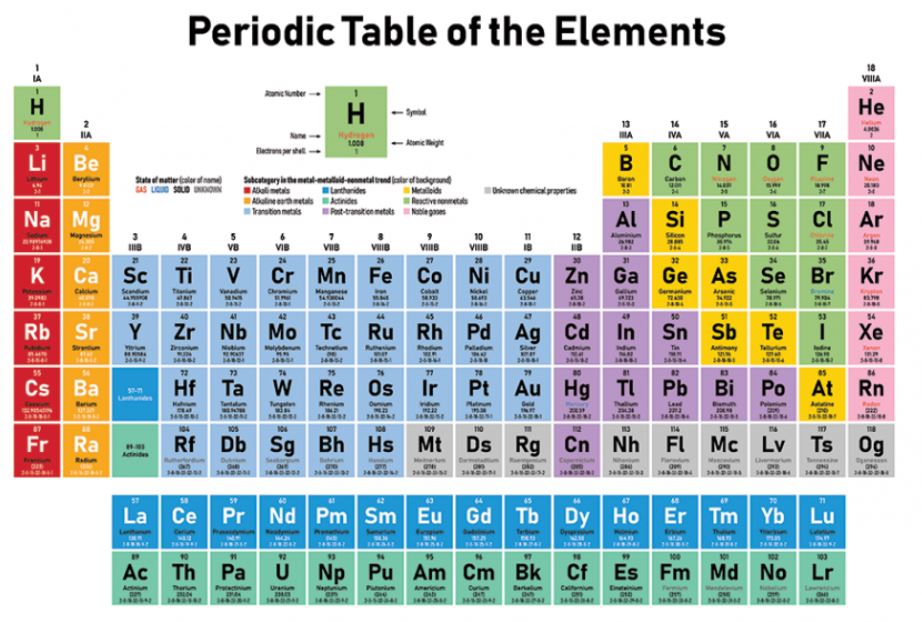
What is a Periodic Table? The periodic table represents the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements known till now that. The chemical elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element) starting from hydrogen with the lowest atomic number (1) and ending at oganesson having the highest atomic number (118).
Arrangement of Elements in Periods and Groups
The tabular arrangement has organized the elements in horizontal rows called periods and vertical columns called groups. The order and number is referred to an elements periodicity.
⦁ The elements in the same group have similar chemical properties due to the similar configuration of valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell). For example, all the elements in group 2A will have 2 electrons in their outermost shell.
⦁ The elements in the same periods will have the same number of atomic orbitals but an ascending order of valence electrons. For example, all the elements in period 1 will have 1 atomic orbital around their nucleus.
Invention of the Periodic Table
The periodic table was first created by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869 who is known as the father of the periodic table. He arranged the 63 elements known at that time into the increasing order of atomic mass in horizontal rows called periods and elements with similar properties were arranged in vertical columns called groups. Later in 1913, the atomic number was discovered as a new property of elements by H. Moseley who observed that atomic number can serve as the basis for the positioning of elements. This is the basis of the periodic law, which states that “The properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic numbers”. This gave rise to the discovery of the modern periodic table.
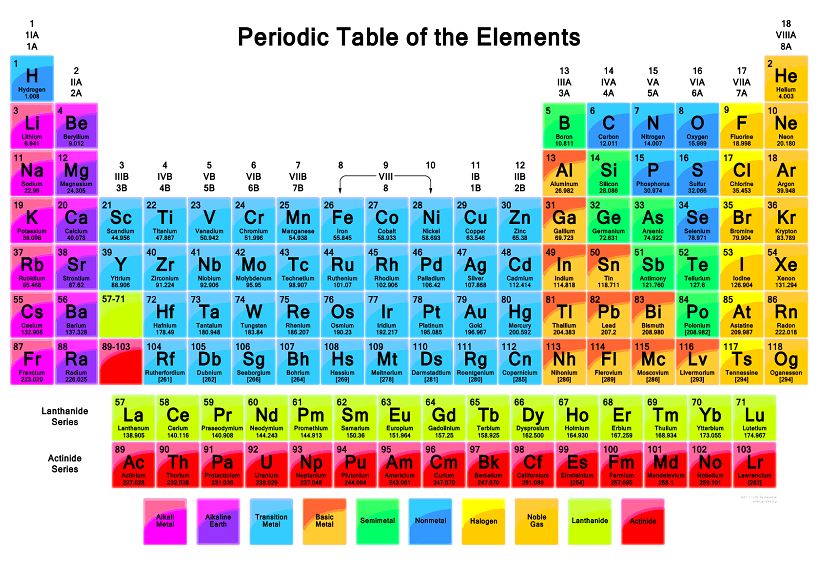

Main Features of Modern or Long Form Periodic Table
⦁ There are seven horizontal rows called periods.
⦁ There are two elements in the first period also known as the short period, 8 elements in the second and third period, 18 elements in the fourth and fifth period (long periods), 32 elements in the sixth period (very long period), and 23 elements in the seventh period which is still incomplete. The series of 14 elements in the sixth and seventh periods are known as lanthanides and actinides respectively.
⦁ There are 18 vertical columns also known as groups, which are arranged from left to right from 1 to 18. All the elements in groups 1, 2, and 13 to 17 are normal, while the elements in groups 3 to 12 are transition elements.
⦁ The elements are divided into four blocks (s, p, d, f) depending on the subshell that carries the valence electron.
Significance of Periodic Table
A periodic table serves great importance for chemistry as it provides significant information about all the known elements and their relations with each other. It is used to predict the chemical and physical properties of elements that are not even discovered yet and their shared characteristics. It has helped scientists to forestall the chemical reactions that can occur and balance the chemical equations in laboratories.
Check out other cool chemistry concepts with other chemistry kits below!