According to the law of conservation of energy in physics, energy cannot be generated or destroyed; it can only be changed from one form to another or moved between objects. This law is covered in physical science, physics, and chemistry studies in middle and high school. For chemistry, energy is a critical concept as it applies to concepts like heat and thermodynamics.

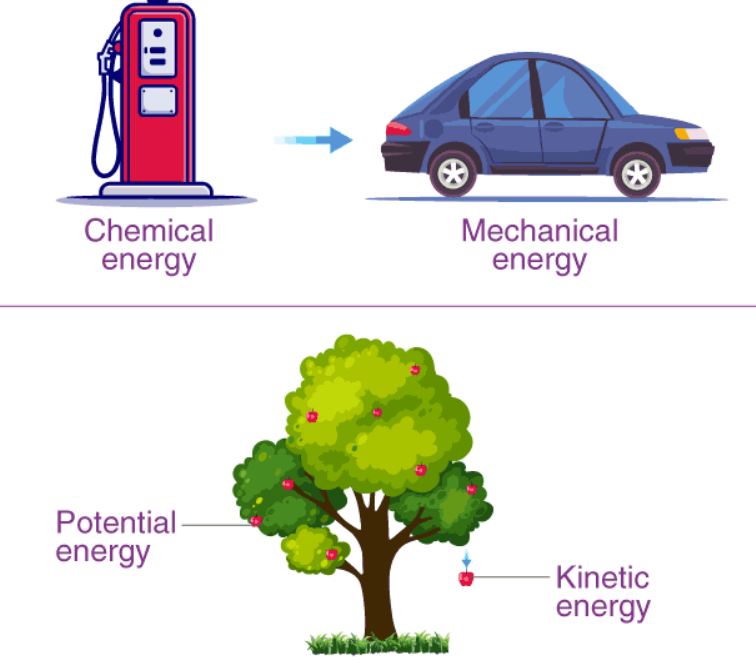
Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
Any entity or system has potential energy because of the position or arrangement of its constituent components. As a result, external elements such as air or height have no effect on it. Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is the energy released by a moving object or system.
Kinetic energy is a form of energy generated by a moving item or particle. The item accelerates and gains kinetic energy when a net force is employed to accomplish energy-transfer work.
P.E + K.E = Constant (Law of Conservation of Energy)
To re-iterate, energy cannot be created or destroyed, according to the law of conservation of energy. It is vital that you comprehend the implications of this law. Claiming that an experiment’s goal is to generate energy is deceptive since it implies that the experiment is attempting to create something that cannot be created. Rather, energy is turned into something valuable on a continuous basis. Solar panels, for instance, do not produce solar energy on their own. They use the energy from the sun’s rays to create a new type of energy (electricity). In a nutshell, energy is constantly being converted from KE. to P.E. and vice versa as per law of conservation of energy. This is also why most perpetual energy or perpetual motion machines stop moving at some point, as they will require a source of energy to move.
Chemical energy transforming to mechanical energy is commonly seen with gasoline and cars, or other forms of combustion engines.
Examples of Law of Conservation of Energy
Bowling
When a moving object collides with something that is stationary, the stationary object moves. This is owing to the fact that a moving object’s kinetic energy cannot be abruptly stopped. Only an impact force may cause an object to move since energy cannot be created or destroyed; impact forces kinetic energy to transfer to other objects.


Dropping Things from Heights
When an object is positioned at a given height, potential energy exists. When an object falls from a great height to the Earth, its potential energy is transformed to kinetic energy by the Earth’s gravitational attraction. When energy is converted from one form to another, the principle of energy conservation is observed.


Chewing Food
When we eat, food is broken down and delivered to the intestines for digestion. Chewing and swallowing food demands mechanical energy. A variety of chemical reactions occur as food reaches the intestines. As a result, the kinetic energy of the meal is transformed into chemical energy. The term calories we commonly hear on food relates to the units of energy provided. Chemical energy gives our body energy which we can be used for a variety of activities, like playing, jogging, and so forth.


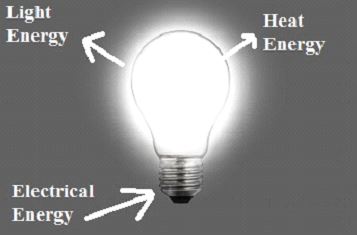
Light Bulb
When the light bulb’s switch is pressed or switched on, an electrical connection is established between the supply unit and the light bulb. As a result of the current flowing through the closed electrical circuit, the light bulb begins to illuminate. After passing through the internal circuitry of the light bulb, electrical energy is converted to light energy. The light bulb is a fantastic example of energy conservation.

Check out other cool chemistry concepts with other chemistry kits below!