We are all surrounded with matter every day. Everything we use, touch, eat, and so on contains matter. Matter is made up of atoms, the smallest objects in the universe, and includes everything that occupies space. It must have both mass and volume properties.
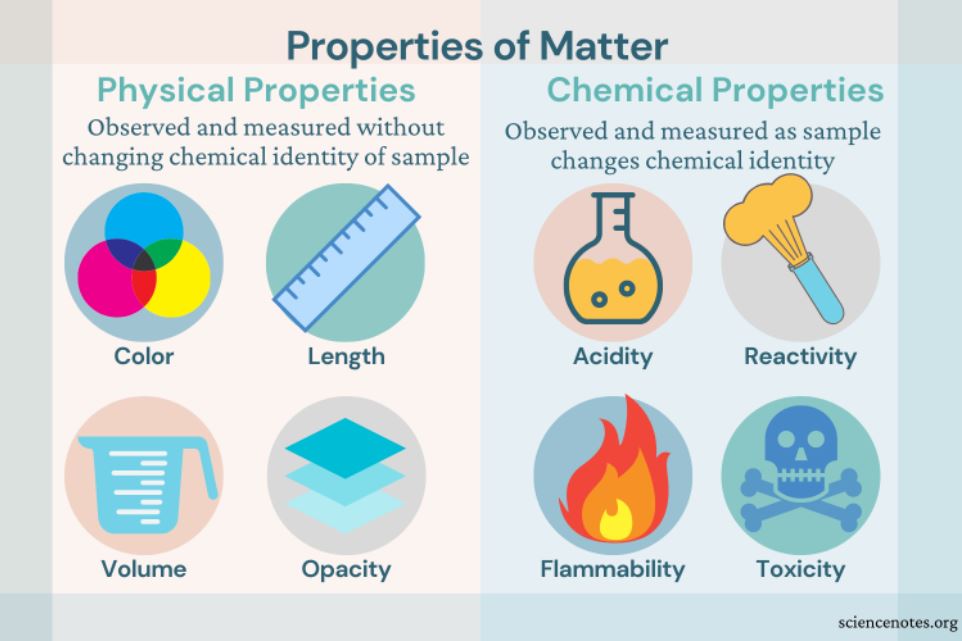
Differentiating between distinct types of matter can be done using its composition and properties. The numerous components of matter and their proportions are referred to as matter composition in chemistry. The features or attributes that distinguish one sample of matter from another are known as matter characteristics or properties. The majority of these properties can be classified as physical and chemical properties.
When the chemical composition of a material changes as a result of a property change the property is referred to as a chemical property. However, a property is a physical property if its alteration does not change the chemical makeup of the substance. When comparing physical and chemical properties, the former may be viewed without changing the chemical composition of a substance, whilst the latter can only be observed by doing so. The flow chart below gives an illustration of how these two categories of properties vary from one another:
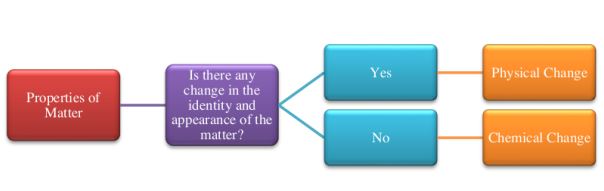

Now let us go through these two primary categories of properties.
Physical Properties
Physical properties of a substance can be quantified without affecting its chemical composition. These characteristics can be used to define a substance’s appearance and size. Different types of matters can also be investigated and compared using physical properties.
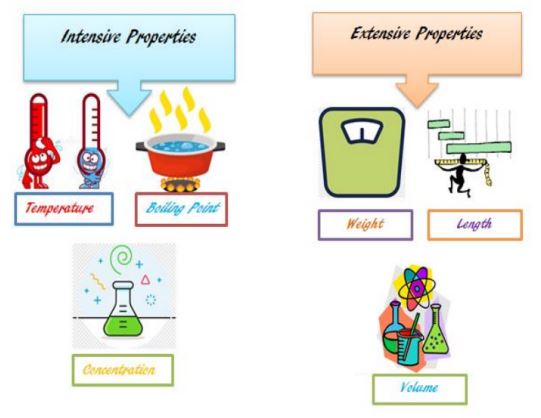
Intensive properties and extensive properties are the two most common forms of physical properties. Physical properties that are amount independent are known as intensive properties. For example, a material’s melting and boiling temperatures are fixed values that are determined only by the kind of substance and not by its quantity. A substance’s concentration has a wide variety of effects on its properties. This indicates that as a material’s amount varies, its overall properties vary as well. Mass, which is a measure of a substance’s quantity, is a complete attribute. Extensive properties are changes in volume, length, or other dimensions produced by a change in the amount of matter.

Chemical Properties
Chemical characteristics can be determined by changes in a material’s chemical makeup. It is no longer the same thing when the chemical makeup of a material changes; it is a new substance. The chemical characteristics of a substance are assessed after it has been subjected to a chemical treatment to check whether any changes have happened. To reveal the sample’s chemical properties, the sample’s structure must be altered.
Compounds’ reactions to acids, bases, water, and other chemicals can be used to determine a substance’s chemical properties. The oxidation state of the elements in a substance changes when it reacts with an oxidizing or reducing agent, for example. As a result, oxidation status may be thought of as a chemical characteristic. Chemical qualities such as elemental reactivity, electronegativity, coordination number, and heat of combustion enthalpy are only a few examples.


Difference between Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter


Check out other cool chemistry concepts with other chemistry kits below!